Food Allergen Course
This Food Allergen training course provides the knowledge needed to keep customers safe from allergens.
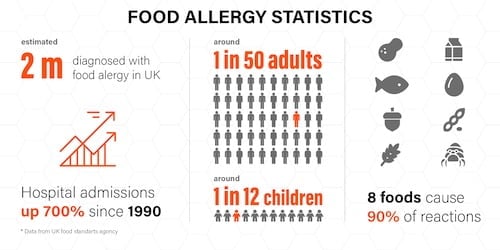
Each year, food allergies affect around two million people in the UK and cause 10 fatalities.
So, all staff working in food businesses must be given appropriate training covering regulations, risks and the best-practice behaviours designed remove the risks to your consumers.
This CPD accredited online Food Allergen course includes an emailed certificate that is also retained online for be retained for employer records.
Course Content
UNIT 1 | FOOD INTOLERANCE
First, we outline the difference between food intolerance and food allergies. Then highlight the risks from allergies.
UNIT 2 | SAFE FOOD SERVICE
Next, we cover how to service food safely. Depending on the type of workplace, this requires a knowledge of labelling laws, menu ingredients and how to deal with customer enquiries.
UNIT 3 | FOOD PREPARATION
The only way to avoid an allergic reaction is to avoid the allergy-causing items. In this unit, we outline best practice for preparing food safely. Including how to avoid the cross-contact of allergenic proteins.
UNIT 4 | EMERGENCY PROCEDURES
In this final unit, we cover what you should you do if a costumer experiences an allergic reaction.
UNIT 4 | QUIZ
Food Allergy Course Certificate

Download and Print Your Certificate
- Written in compliance with Natasha’s Law
- Developed by qualified health and safety professionals Accredited by CPD – learn more about CPD here
- Last Updated March 2025
- To gain the certificate you must complete the assessment which involves 20 questions.
- You can access our LMS any time to reprint certificates, check and set pass marks and act as proof of a commitment to ongoing legal compliance.
- The online Food Allergens certificate is valid for 3 years.
How to use the Echo3 Platform
Individual Learners

Benefits for Individuals
-
Engaging video-based content
-
Learner dashboard included
-
Instant access after payment
-
Free course retakes
-
Shareable digital certificate
 QR Code Certificate
QR Code Certificate



Bulk Buying Discounts
10 Courses
50 Courses
100+ Courses
Course Preview
Echo3 courses include engaging motion-graphic video content, with full english subtitles
What are the Food Allergy course objectives?
 The Food Allergen course objectives include.
The Food Allergen course objectives include.
Recognise Allergens. Identify the 14 allergens, their sources, and common foods containing these allergens.
Legal Compliance. Understand the latest labelling laws and regulations relating to allergens in cafes and restaurants.
Symptom Recognition. Recognise symptoms of allergic reactions and understand their severity, enabling timely and appropriate responses.
Risk Management. Learn how to manage and minimise risks related to food allergies in different environments, such as restaurants, kitchens, and homes.
Effective Communication. Learn how to communicate clearly to customers with food allergies and accommodate their needs.
Emergency Response. Acquire knowledge about emergency procedures and responses in case of allergic reactions, including the use of epinephrine auto-injectors.
Prevention and Cross-Contamination. Understand methods to prevent cross-contamination and ensure safe food handling to avoid allergic reactions. We offer a dedicated course in Preventing Cross-Contamination that covers more detail including kitchen design.
Who should take this food allergen course?
 This online Food Allergy training course has been designed for.
This online Food Allergy training course has been designed for.
- All food preparation and service staff.
- Managers and supervisors of food businesses
The Echo3 Food Allergy Awareness course is invaluable for many individuals including, but not limited to.
All professionals in the food industry. This includes chefs, cooks, servers, and managers. Each must understand the risks from allergens, to ensure safe food handling, and minimising cross-contamination risks.
Health practitioners and caregivers. Knowing how to managing allergies properly will help them better support and care for allergic individuals.
All those with Safeguarding or Child Protection responsibilities will benefit from this Allergen Awareness course. They will acquire the knowledge essential for managing allergies at home, schools, and social gatherings.
Everyone involved in hospitality and event planning, will learn to help create inclusive environments by accommodating diverse dietary needs.
Essentially, anyone seeking to prevent allergic reactions, ensure compliance with regulations, and foster safety should consider undertaking an online food allergen course.
Why is allergen training important?
In the UK, food allergies affect about 2-3% of adults and 5-8% of children, with these numbers rising over recent decades. The impact goes beyond just physical symptoms – there are significant economic costs to the healthcare system, operational challenges for businesses, and profound social and psychological effects on individuals who must constantly navigate potential risks to their well-being.
Appropriate Food Allergy training is necessary to comply with food safety regulations and food standards agency requirements. And ensure employees have the knowledge needed to keep customers safe.
What is Natasha’s law?
The UK’s allergen labeling requirements have evolved significantly, especially after Brexit and the introduction of Natasha’s Law. These regulations aim to ensure consumers with allergies can make safe food choices through clear, consistent information.
The tragic case of Natasha Ednan-Laperouse, who died on a flight from Heathrow to France in 2016 after eating a baguette containing sesame seeds that wasn’t labeled on the packaging, which contained no allergen information because it was prepared on-site and thus exempt from individual labelling requirements.
This tragedy directly led to Natasha’s Law, which closed the labelling loophole for Pre-Packed for Direct Sale (PPDS) foods, ensuring all ingredients and allergens must now be clearly listed regardless of where the food was packaged.
How do allergies and intolerances differ?
When we talk about food hypersensitivities, it’s important to understand the distinctions.
Food allergies involve the immune system reacting to certain proteins, often causing rapid and sometimes severe reactions.
This differs from food intolerances, which typically don’t involve the immune system and often affect the digestive system with more delayed symptoms. Then there’s celiac disease, an autoimmune condition triggered specifically by gluten, and various chemical sensitivities to food additives or naturally occurring compounds like histamine.
When someone experiences an allergic reaction, the symptoms can range from mild such as itching, hives and swelling. To moderate such as breathing difficulties and dizziness. To severe, which may present as anaphylaxis which is a potentially life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical attention. This is why understanding and properly managing allergens is not just a regulatory requirement but a critical safety issue.
What are the big 14 allergens?
UK legislation requires special attention to 14 major allergens that must be clearly identified in food products. These include
- cereals containing gluten,
- crustaceans,
- eggs,
- fish,
- peanuts,
- soybeans,
- milk,
- tree nuts,
- celery,
- mustard,
- sesame seeds,
- sulphites (above certain concentrations),
- lupin,
- and molluscs.
Each of these allergens presents unique challenges for food handling and production.