MANAGING MANUAL HANDLING RISKS
This article outlines the risks from manual handling and how to appropriately reduce manual handling risks in the workplace. All those responsible for the health of employees at work will benefit from reading this.
Topics covered
- What is Manual Handling
- The Hazards from Manual handling
- Employer and Employees Duties
- Individual Risk Factors
- Manual Handling Risk Assessments
- Safe Manual Handling Techniques
What is Manual Handling?
Manual handling is the transporting or supporting of a load by one or more individuals. This include lifting, putting down, pulling, carrying or moving of a load which by reason of its characteristics, involves risks, particularly of back injury.
What are the hazards from Manual Handling?
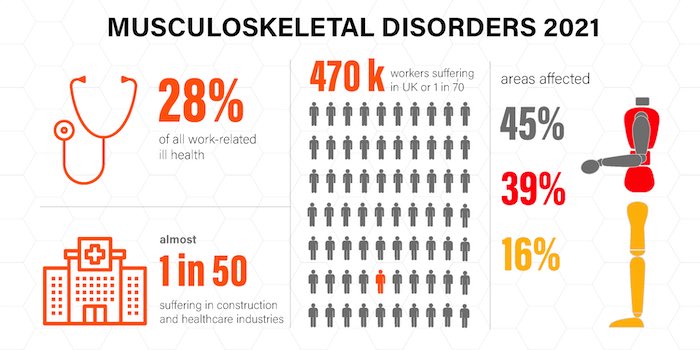
The main hazards from lifting at work are Musculoskeletal Disorders, also known as MSDs. The musculoskeletal system refers to all of our soft tissue that attaches to bones so we can move. For example; muscles, joints, tendons, cartilage and nerves. MSDs are injuries of any of these components.
This risks of MSDs in the workplace are large and should be taken seriously by all employers. Especially in businesses where frequent lifting occurs, like construction sites.
In fact, MSDs are the biggest cause of absenteeism in the UK workplace. Over the 2022/23 RIDDOR reporting period 1.8 million UK workers suffered from work-related ill health. 27% of these were due to musculoskeletal disorders. MSDs are often long-term injuries. Costing employers greatly due to staff being off work as a result.
MSDs, occur not just through lifting.
For example; staff could trip while carrying a load or drop a heavy object on their foot.
Other risk factors include,
- The amount of times workers have to pick up or carry an item
- The distance they carrying them
- The height they are picking it up from or putting it down at
- And any twisting, bending stretching or other awkward posture you may get into, all increase the risk of MSDs
Employer’s Manual Handling Duties

The regulation that covers manual handling is called the 1992 Manual Handling regulations. It places the follow duties on employers.
- Provide a safe place at work
- Undertake a risk assessment
- Provide welfare facilities
- Provide emergency procedures
- Provide staff adequate training, information, and supervision
- Provide staff adequate equipment that is maintained in a safe condition
- Provide PPE where hazards cannot be eliminated
- Report incidents/accidents
Employees duties with respect to manual handling?

Employees also have responsibilities. They must;
- Take reasonable care of their own safety and that of others
- Comply with legislation and co-operate with the employees statutory duties
- Attend training and undergo assessments. Then adhere to all safety instructions detailed in training or by supervisors.
- Use PPE correctly
- Report hazards, accidents, etc
- And not misuse any equipment that is provided for securing their health and safety
- Do not attend work under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Consider the Individual
Individuals can have characteristics that increase their own risks of MSDs.
As an employer you must consider these and not ask someone to undertake a task which is unsafe for them.
Individual Risk factors include:
Overweight – the extra weight puts pressure on the musculoskeletal system especially the spine and the lower limbs.
Being pregnant – the extra weight of carrying a baby and hormonal changes that affect the ligaments can increase risk of injury. Employers should take special measures to protect staff that are pregnant and required to lift at work.
Long-term use of medication known to weaken bones e.g. some cancer treatments.
Previous injury – can result in loss of fitness and decreased activity which is now thought to be a major cause of persisting/recurring symptoms. Reconditioning is now considered an important part of injury recovery.
Poor posture at home and work e.g. bending awkwardly or for long periods, slouching in chairs, driving in a hunched position or driving for long periods without taking a break, twisting awkwardly.
Sedentary behaviour – remaining seated or lying down for extended periods of time, for much of the day. Encourage more movement at work will reduce this risk factor.
Evidence suggests that keeping your musculoskeletal system strong and supple can reduce these risks.
Most experts now agree injuries heal quicker if movement is maintained as much as possible even if it causes some discomfort.
Manual Handling Risk Assessments

It is a legal requirement for all employers to assess the potential risks from manual handling activities. This process is called risk assessment.
A risk assessment is a careful examination of what, in the workplace, could cause harm to people, so that the employer can weigh up whether they have taken enough precautions or should do more to prevent harm.
Conducting A Manual Handling Risk Assessment?

Many organisations follow the T.I.L.E template when thinking about manual handling risks in their workplace. TILE standards for; Task, Individual, Load & Environment.
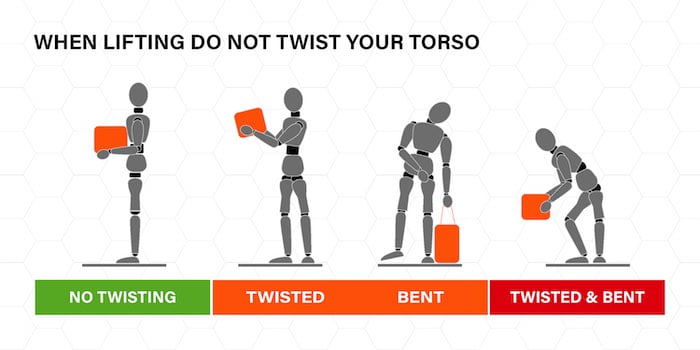
Task – this looks at what the person is attempting to do, for example does it require; Any twisting, stooping or reaching? Is there excessive physical effort required and excessive lowering or lifting?
Individual – this looks at the person. Have they received adequate training and; Are they physically capable of successfully completing the task? Are there any potential health issues that may restrict them from carrying out the task e.g. pregnancy or disability. Is PPE required when carrying out the task?
Load – this looks at what the person is attempting to move. Is it too large or too heavy? Is it too hot, cold, greasy or sharp? Does the object demand an awkward or difficult grip and is the object unstable with content that is likely to move around? Does it require bending or twisting of the trunk?
Environment – this looks at the surroundings. Is there sufficient room for movement? Is there an uneven or slippery floor. Is there adequate lighting allowing for good visibility? Are there comfortable working conditions, for example is it too hot or cold, or is it a dusty environment?
There are plenty of template risk assessment documents online that you can download for free which will help you complete this process easily.
Implement the Risk Assessment

Your manual handling risk assessment will highlight the activities in your workplace that are most likely to lead to harm.
Now, First try to eliminate these activities. So remove the requirement to lift.
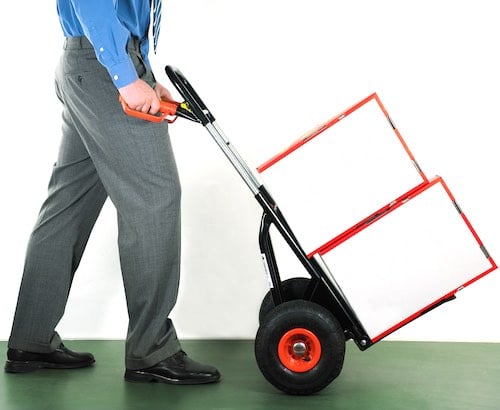
Secondly, if removal is not possible next you could invest in mechanical aids such as pump trucks or chutes.
Thirdly if lifting in unavoidable provide them with manual handling training so they know how to lift safely.
Fourth, periodically review and improve your risk assessment and work procedures based on staff feedback and any incidents.
Manual handling Training
Manual handling training provides staff with an understanding of how to lift safely, minimising the chance that they develop an MSD.
Manual handling training for staff will provide them to knowledge to lift safely. For example it will likely include the 8 principles of safe manual handling, which are;
- Assess the task, the individual, the load and the environment
- Have a broad, stable base
- Bend at your knees
- Keep you back straight
- Have a firm palmer grip
- Keep your arms in line with trunk
- Weight close to your centre of gravity
- Turn feet in direction of travel
Safe Manual Handling Techniques
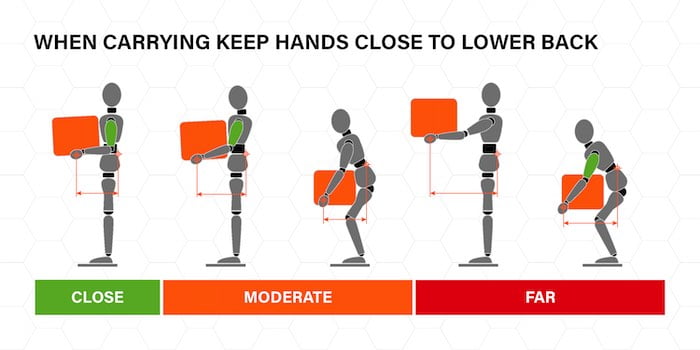
When carrying an object, always keep the load close to your body by keeping your arms tucked in. Don’t change your grip or the load unless the weight is supported (e.g. trolley, table). Don’t twist your body, stoop, bend or lean back.
If you must change direction, move your feet instead. Don’t block your vision by carrying something that is too big. Use a mechanical aid or get help if you need it. Face the spot where the load will rest, by turning your feet and whole body in that direction.
Different Types of Manual Handling
Lifts from Height
Ideally you should avoid employees having to lift anything above their shoulders.
However, if this is not possible, lighten the load by dividing it into smaller loads. Stand on something sturdy (not a chair), with one foot in front of the other, unless you are using a stepladder.
Always look to use a mechanical aid where possible and if in doubt ask for help, particularly if the load is heavy or awkward. When lowering from a high place you should also take extra care. Test the load’s weight by pushing up on it. Check to see if it will shift when you lift it.
Advantages of Pushing
Pushing is easier than pulling (you can see what you are doing), but ensure that you don’t overload the truck or trolley and make sure you can see over the top. Stay close to the object and keep control over its movement. Take special care on slopes. Get a good grip of the handle and keep your elbows in.
Pulling a Load
Although you can pull a load, it is worth noting that this carries more risk than pushing a load. You should avoid pulling if possible, because looking over your shoulder twists your spine and this can lead to injury.
Conducting a Team Lift
When conducting a team lift, try to lift with someone of a similar height. Choose one person to give instructions. Make sure both people have the same palmer grip on the load. Lift from the hips at the same time, then raise the load to the right level.
Move smoothly and at the same time. It is important that you plan the execution of the task. Also, as a team, you must lift in sync with each other. This is best when one person assumes control and can give orders to the others. To help avoid confusion, it is best if a set of commands is agreed on as this ensures that everything occurs in a smooth manner.
Contact Us
Contact us is you have any question about how Echo3 may be able to help improve training in your workplace.








