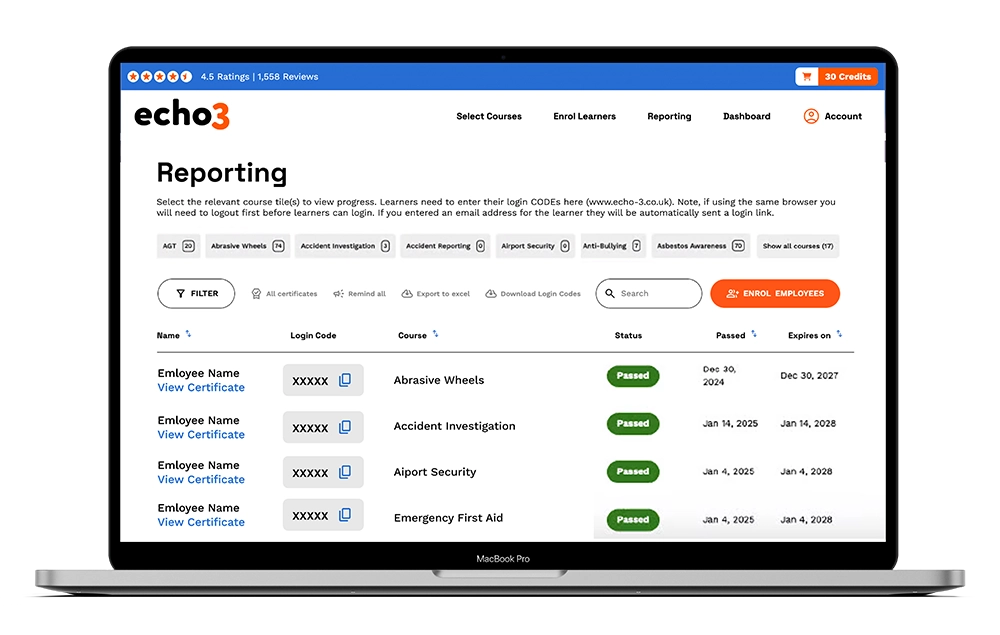
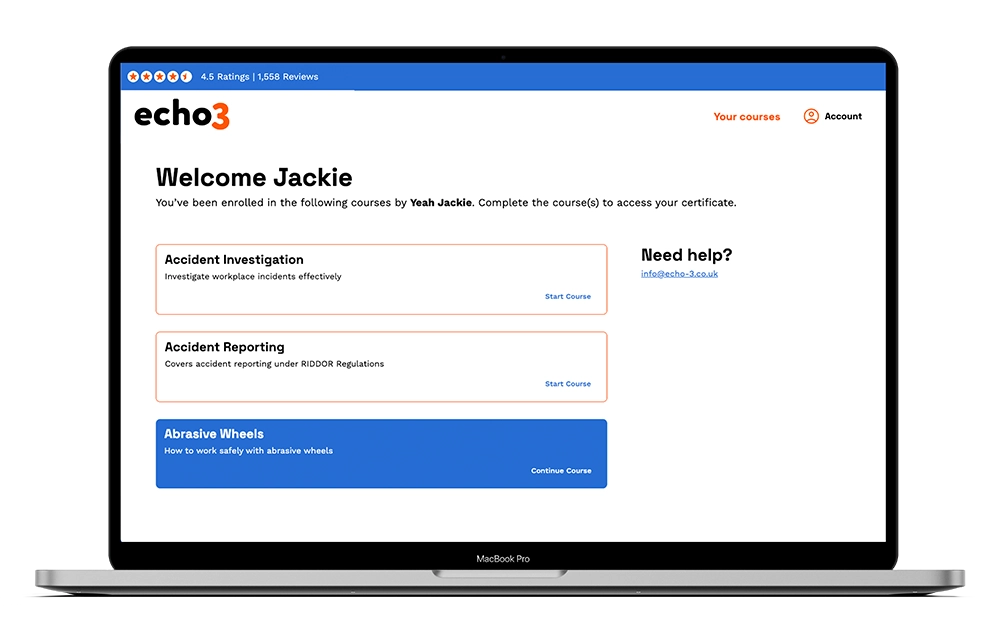
Lone Working Course
 A lone worker is anyone who works by themselves without direct supervision, including employees, contractors, and the self-employed.
A lone worker is anyone who works by themselves without direct supervision, including employees, contractors, and the self-employed.
In the UK, it’s estimated that 1 in 5 workers now fall into this category. This includes a wide range of roles, such as delivery drivers, community nurses, engineers, retail staff, and construction workers. The rise in lone working has been driven by advances in technology and accelerated by changes brought about during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Working alone can present additional risks due to the absence of immediate support in the event of an emergency. Situations involving first aid incidents, fire, or harassment can pose greater danger when help is not readily available.
The Echo3 Online Lone Working Course equips individuals with the knowledge and tools to manage these challenges confidently and safely. Designed for staff across a variety of industries, the course raises awareness of the risks faced by lone workers and outlines best-practice strategies to reduce them.
Key topics covered include:
- Conducting effective risk assessments
- Implementing lone working safety protocols
- Establishing reliable communication methods
- Preparing for and responding to emergencies
By completing this Lone Working course, learners will gain the skills to stay safe while working alone, contribute to a proactive safety culture, and help their employers meet legal and regulatory responsibilities.
 Lone Working Course Content
Lone Working Course Content
Unit 1 – Introduction to Lone Working
This introductory module covers the fundamentals of lone working, including who qualifies as a lone worker, the responsibilities involved, and how to carry out effective risk assessments.
Unit 2 – Risk of Lone Working
This unit highlights common hazards faced by lone workers across industries such as healthcare, retail, cleaning, sales, construction, and home-based work. By increasing awareness of these potential risks, staff will be better equipped to implement effective measures to protect themselves.
Unit 3 – Lone Working Control Measures
In this final unit, we explore the key control measures that both employers and employees can implement to enhance safety, including training, supervision, safety equipment, first aid, Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), and emergency planning.
Unit 4 – Quiz
The course concludes with a 10-question multiple-choice quiz. Achieve a score of 80% or higher to demonstrate your understanding of the key learning objectives and receive your CPD-accredited Lone Working certificate via email. Learners are allowed to retake the quiz if needed.
Lone Working Course Certificate

Download and Print Your Certificate
- Written in compliance with the HSE Act 1974 and the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999.
- Developed by qualified health and safety professionals
- Accredited by CPD – learn more about CPD here
- Last Updated March 2025
- To gain the certificate you must complete the assessment which involves 10 questions.
- The online Lone Working certificate is valid for 3 years.
Course Preview
Echo3 courses include engaging motion-graphic video content, with full english subtitles
Reviews
How to Get Certified in 3 Steps
Individual Learners

Benefits for Individuals
-
Engaging video-based content
-
Learner dashboard included
-
Instant access after payment
-
Free course retakes
-
Shareable digital certificate
 QR Code Certificate
QR Code Certificate




Bulk Buying Discounts
What are the lone working course objectives?
 The course is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of safety practices tailored specifically for individuals who work alone. The objectives of the course are to:
The course is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of safety practices tailored specifically for individuals who work alone. The objectives of the course are to:
- Risk Assessment– Explain the purpose and importance of risk assessments for lone workers, and the need to follow control measures to reduce potential hazards.
- Safety Protocols– Provide practical knowledge of safety controls and procedures that help mitigate the unique risks associated with working alone.
- Communication Strategies– Teach effective methods for maintaining communication and accessing support in routine situations or emergencies.
- Legal Compliance– Ensure learners understand the legal responsibilities and regulatory standards related to lone working.
- Emergency Procedures– Equip individuals with the skills to respond to emergencies confidently and make informed, independent decisions.
- Enhanced Preparedness– Encourage a proactive mindset to help workers anticipate, assess, and manage the challenges of working alone.
Overall, the course aims to empower individuals with the knowledge, skills, and confidence needed to work safely, independently, and in compliance with best practices and legal requirements.
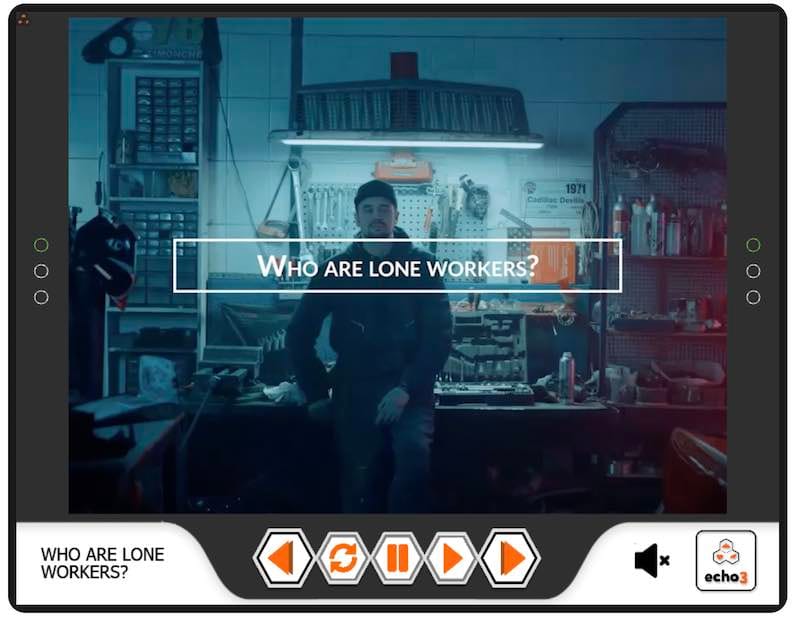
Who are lone workers?
 Lone workers are classed as anybody who works alone, including staff, contractors, and the self-employed.
Lone workers are classed as anybody who works alone, including staff, contractors, and the self-employed.
Lone workers fall into two categories, Fixed Site Workers and Mobile Workers.
1. Fixed Site Workers
These individuals work alone within a fixed location, either during normal hours or outside of them. Examples include, a person working alone in a small workshop, petrol station, or retail shop.

2. Mobile Workers
These workers operate away from a central base or head office and may not have direct supervision. Examples include:
- Individuals working in remote areas, such as agriculture or forestry
- Construction, maintenance, or cleaning staff
- Home-based workers
- Staff working outside normal hours, such as security personnel or night-shift petrol station attendants
What are the lone working hazards?
Transportation employees
In the transport sector, Lone workers like bus or taxi drivers could be exposed to robberies , road accidents, road rage incidents, sprain and strain injuries, verbal and physical assault and anti-social behaviour from angry passengers.
Health Care
Lone healthcare workers such as carers, are mainly exposed to lifting injuries and drug handling hazards like needle stick injuries and blood borne pathogens.
But also again they are at risk of robberies, verbal and physical assault from patients and drug handling.
Retail
Lone retail workers can be exposed to lifting injuries, and again robberies and verbal and physical assault from customers.
Cleaning
Cleaners often work with hazardous substances like bleach. So lone working cleaners need to be trained about the nature of the substances and materials they work with, the risks created by exposure to those substances and the precautions to take.
The construction industry
The construction sector is one of the world’s most dangerous industries, accounting for numerous workplace injuries and fatalities each year. Lone construction workers can be exposed to falling from height, lifting and other work-related injuries, theft of equipment and operating equipment.
Homeworkers
Homeworkers are those who use their home as their place of work for the majority of the time. An employer has the same responsibility for home workers as for any other employees.
When working with Display Screen Equipment or DSE it is important for a homeworker to adjust their work station to a comfortable position and take frequent short breaks from work.
Related Courses
Defensive Driving – know the safe driving mindset
Emergency First Aid at Work – how to respond to first aid emergencies
Fire Safety and Prevention – how to prevent and respond to fires at work
Forestry First Aid +F – know forest first aid
Lyme Disease Awareness – how to stay safe where ticks could be present
Preventing Violence at Work – how to reduce the chance of violence at work
Risk Assessment – how to undertake risk assessments
Van Driver Safety – how to drive and deliver goods safely
Working From Home – understand safety basics when working from home
Access all Echo3 courses using credit.












 Lone Working Course Content
Lone Working Course Content